Unlocking the Power of Agile Project Management: Myths,
Unlocking the Power of Agile Project Management: Myths, Realities, and Best Practices In today's fast-paced, ever-changing business landscape, trad...
Unlocking the Power of Agile Project Management: Myths, Realities, and Best Practices
In today's fast-paced, ever-changing business landscape, traditional project management approaches often struggle to keep up with the rapidly evolving needs of organizations. Enter Agile project management – a flexible, iterative, and customer-centric approach that has revolutionized the way teams plan, execute, and deliver projects. However, like any transformative methodology, Agile project management is often misunderstood and surrounded by misconceptions. In this comprehensive article, we'll dive deep into the myths and realities of Agile, providing you with a clear understanding of its principles, benefits, and best practices to help you unlock its full potential.
Myth 1: Agile is only for software development
One of the most persistent myths about Agile project management is that it is solely applicable to software development teams. While Agile originated in the software industry, its principles and practices can be effectively applied to a wide range of industries and project types, from marketing and product development to construction and manufacturing.
The core principles of Agile, such as iterative planning, continuous feedback, and adaptability, are universally beneficial across various sectors. In fact, many non-tech organizations have successfully adopted Agile methodologies, such as Scrum or Kanban, to improve their project delivery, increase collaboration, and respond more quickly to changing market demands.
Case in point: Spotify, a leading music streaming service, has implemented an Agile framework called ""Spotify Model"" to manage its product development and engineering teams. This approach has enabled Spotify to rapidly iterate on new features, quickly address user feedback, and maintain a competitive edge in the highly dynamic music industry.
Myth 2: Agile is all about speed and sacrifices quality
Another common misconception is that Agile project management is solely focused on speed and delivery, often at the expense of quality. While it's true that Agile emphasizes rapid iterations and frequent releases, this doesn't mean that quality is compromised.
In fact, Agile methodologies place a strong emphasis on continuous testing, feedback, and iterative improvement. By breaking down projects into smaller, manageable increments, Agile teams can identify and address quality issues early on, rather than waiting until the end of the project. This approach allows for rapid course corrections and ensures that the final product meets or exceeds the desired quality standards.
Moreover, Agile encourages a collaborative and transparent work environment, where team members work closely together to identify and resolve quality-related concerns. This collaborative approach, combined with the focus on continuous improvement, helps to maintain and even enhance the overall quality of the project deliverables.
A great example of Agile's focus on quality is the case of Lego, the renowned toy manufacturer. Lego has successfully adopted Agile practices in its product development process, allowing the company to quickly respond to customer feedback, test new product ideas, and ensure the highest level of quality in its iconic toy sets.
Myth 3: Agile is a one-size-fits-all approach
Another common misconception about Agile project management is that it is a rigid, one-size-fits-all approach. In reality, Agile is a flexible framework that can be tailored to the unique needs and requirements of different organizations, teams, and projects.
Agile methodologies, such as Scrum, Kanban, and Lean, provide a set of principles and practices that can be adapted and combined to suit the specific context of a project. For example, a marketing team may use a Kanban-based approach to manage their content creation and campaign planning, while a product development team might prefer a Scrum-based framework to manage their software releases.
The ability to customize Agile to fit the needs of the organization is one of its key strengths. By adopting a ""horses for courses"" approach, teams can leverage the benefits of Agile while ensuring that the implementation aligns with their unique organizational culture, team dynamics, and project requirements.
A great example of this adaptability is the case of Spotify's ""Spotify Model,"" which we mentioned earlier. While based on Agile principles, the Spotify Model has been specifically designed to address the unique challenges and needs of a large-scale, rapidly evolving technology company like Spotify.
Myth 4: Agile is only for small, co-located teams
Another common misconception about Agile project management is that it is only suitable for small, co-located teams. While it's true that Agile thrives in environments where team members can collaborate closely and communicate effectively, it can also be successfully implemented in larger, distributed teams.
Advances in communication and collaboration technologies, such as video conferencing, project management tools, and virtual whiteboards, have made it possible for Agile teams to work effectively across multiple locations and time zones. By leveraging these tools and implementing best practices for remote collaboration, Agile teams can maintain the same level of transparency, coordination, and adaptability as their co-located counterparts.
For example, Atlassian, the software development company behind popular tools like Jira and Confluence, has successfully scaled Agile practices across its global, distributed teams. By fostering a strong Agile culture, investing in collaboration tools, and implementing effective remote work strategies, Atlassian has been able to deliver complex software projects with the speed and flexibility that Agile is known for.
Myth 5: Agile is all about the process, not the people
One of the most persistent myths about Agile project management is that it is solely focused on the process, rather than the people. In reality, Agile places a strong emphasis on the individuals and interactions within a team, recognizing that the success of a project depends heavily on the collaboration, communication, and empowerment of the people involved.
Agile methodologies, such as Scrum, explicitly value ""individuals and interactions over processes and tools,"" as stated in the Agile Manifesto. This means that Agile teams prioritize building strong, cross-functional teams, fostering open communication, and empowering team members to make decisions and take ownership of their work.
By prioritizing the human element, Agile teams can unlock greater creativity, innovation, and problem-solving capabilities. This, in turn, leads to higher levels of engagement, productivity, and overall project success.
A prime example of this people-centric approach is the case of Spotify's engineering teams. Spotify has built a strong Agile culture that emphasizes autonomy, trust, and continuous learning, enabling its teams to thrive and deliver exceptional results in a rapidly evolving industry.
Myth 6: Agile requires a complete overhaul of existing processes
Another common misconception about Agile project management is that it requires a complete overhaul of an organization's existing processes and structures. While it's true that adopting Agile may necessitate some changes, it doesn't always mean a complete transformation from the ground up.
In fact, many organizations have successfully implemented Agile practices by gradually integrating them into their existing project management frameworks. This ""hybrid"" approach allows teams to leverage the benefits of Agile, such as increased flexibility and customer responsiveness, while maintaining the stability and familiarity of their current processes.
For example, a company might start by introducing Agile practices, such as daily standups and iterative planning, into their traditional waterfall-based project management approach. Over time, they can then gradually expand the Agile elements, eventually transitioning to a more comprehensive Agile framework, such as Scrum or Kanban.
The key is to approach Agile adoption with a growth mindset, focusing on incremental improvements and continuous learning, rather than a complete and immediate overhaul. This gradual approach helps to minimize disruption, build buy-in from stakeholders, and ensure a successful Agile transformation.
Myth 7: Agile is only suitable for IT and software projects
As mentioned earlier, one of the most persistent myths about Agile project management is that it is solely applicable to the IT and software development industries. While Agile did indeed originate in the tech sector, its principles and practices can be effectively applied to a wide range of industries and project types.
From marketing and advertising to manufacturing and construction, Agile methodologies have been successfully adopted by organizations across various sectors. By focusing on iterative planning, continuous feedback, and adaptability, Agile teams can effectively manage complex projects, respond to changing market conditions, and deliver high-quality results in a wide range of industries.
A great example of Agile's versatility is the case of Procter & Gamble, the consumer goods giant. P&G has implemented Agile practices in its product development and innovation processes, allowing the company to rapidly prototype, test, and iterate on new product ideas. This Agile approach has enabled P&G to stay ahead of the curve and maintain its competitive edge in the fast-paced consumer goods market.
Myth 8: Agile is all about eliminating planning
Another common misconception about Agile project management is that it eliminates the need for planning altogether. While it's true that Agile emphasizes flexibility and adaptability over rigid, long-term planning, it doesn't mean that planning is entirely absent from the Agile process.
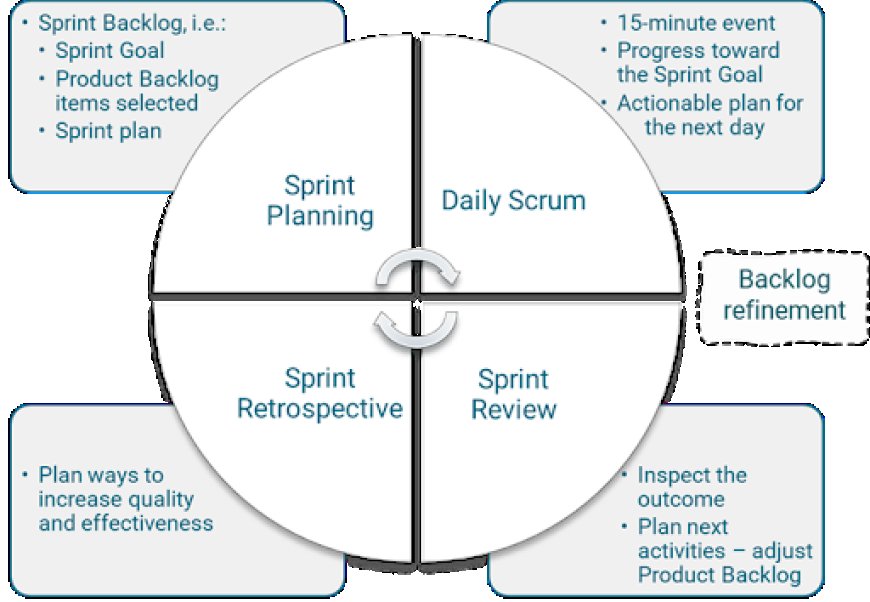
In fact, Agile methodologies, such as Scrum, incorporate various planning activities, including sprint planning, release planning, and backlog grooming. These planning sessions allow Agile teams to define their goals, prioritize tasks, and create a roadmap for delivering value to their customers.
The key difference in Agile planning is the focus on short-term, iterative planning rather than long-term, detailed planning. Agile teams plan in smaller, manageable increments, allowing them to adapt to changing requirements and priorities as they arise. This approach helps to ensure that the team is always working on the most valuable and relevant tasks, rather than being locked into a rigid, long-term plan that may no longer align with the project's needs.
A great example of Agile planning in action is the case of Lego's product development process. Lego's Agile teams engage in regular sprint planning sessions to define their goals, prioritize features, and create a roadmap for their upcoming product releases. This iterative planning approach has enabled Lego to quickly respond to customer feedback, test new ideas, and bring innovative toy sets to market faster than their competitors.
Agile Project Management: Best Practices for Successful Implementation
Now that we've debunked the common myths surrounding Agile project management, let's explore some of the best practices for successfully implementing Agile within your organization:
1. Establish a strong Agile culture
Successful Agile adoption starts with building a culture that embraces the core values and principles of Agile. This includes fostering open communication, encouraging experimentation and learning, and empowering team members to take ownership of their work. By creating an Agile-friendly environment, you can help to ensure that the transition to Agile is smooth and sustainable.
2. Provide comprehensive Agile training and coaching
Transitioning to Agile requires a significant shift in mindset and skillset for many organizations. Investing in comprehensive Agile training and coaching for your teams can help to ensure that they understand the Agile principles, practices, and tools, and are equipped to implement them effectively.
3. Start with a pilot project
Rather than attempting a full-scale Agile transformation across your entire organization, it's often best to start with a pilot project. This allows you to test the Agile approach in a controlled environment, identify any challenges or pain points, and refine your implementation strategy before scaling it up.
4. Embrace a continuous improvement mindset
Agile is all about adapting and improving over time. Encourage your teams to continuously reflect on their processes, identify areas for improvement, and experiment with new Agile practices. This continuous improvement mindset will help to ensure that your Agile implementation remains effective and relevant as your organization and project needs evolve.
5. Align Agile with organizational goals
Successful Agile implementation requires aligning your Agile practices and processes with the overall strategic goals and objectives of your organization. By ensuring that your Agile efforts are directly supporting your business priorities, you can maximize the impact and value of your Agile transformation.
6. Foster cross-functional collaboration
Agile thrives on cross-functional collaboration, where team members with diverse skills and expertise work together to achieve project goals. Encourage your teams to break down silos, share knowledge, and leverage each other's strengths to deliver better results.
7. Implement effective Agile tools and technologies
Agile project management often relies on a suite of tools and technologies to support collaboration, communication, and visibility. Invest in Agile-friendly tools, such as project management software, virtual whiteboards, and communication platforms, to help your teams work more efficiently and effectively.
8. Measure and track Agile performance
To ensure the ongoing success of your Agile implementation, it's essential to measure and track key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with your Agile goals. This might include metrics such as sprint velocity, customer satisfaction, and team productivity, which can help you identify areas for improvement and demonstrate the value of your Agile efforts.
By following these best practices, you can unlock the full potential of Agile project management and drive tangible, sustainable results for your organization.
Conclusion
Agile project management is a powerful and versatile approach that can transform the way your organization plans, executes, and delivers projects. By understanding and debunking the common myths surrounding Agile, you can embrace its true benefits and effectively implement it within your organization.
From breaking down the misconception that Agile is only for software development to recognizing the importance of people and continuous improvement, this comprehensive guide has provided you with the insights and best practices you need to unlock the power of Agile project management.
Remember, Agile is not a one-size-fits-all solution, but a flexible framework that can be tailored to the unique needs and requirements of your organization. By adopting a growth mindset, fostering a strong Agile culture, and continuously learning and improving, you can ensure that your Agile implementation delivers tangible, long-lasting results.
So, are you ready to embrace the power of Agile project management and take your organization to new heights? Start your Agile journey today and unlock the key to project success in the modern business landscape.
KEYWORDS: Agile project management, Agile methodologies, Scrum, Kanban, Agile transformation, Agile best practices, Agile myths, Agile implementation
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0