The Ultimate Guide to Student Loan Repayment Plans
The Ultimate Guide to Student Loan Repayment Plans Navigating the world of student loan repayment can be a daunting task,
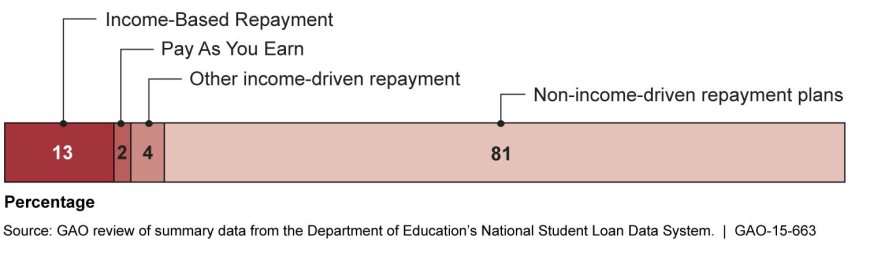
The Ultimate Guide to Student Loan Repayment Plans
Navigating the world of student loan repayment can be a daunting task, but with the right information and guidance, you can find the best plan to manage your debt effectively. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the various student loan repayment options available, their eligibility requirements, and the benefits and drawbacks of each plan. Whether you're just starting to repay your loans or are looking to optimize your current repayment strategy, this guide will provide you with the insights you need to make informed decisions.
Understanding Your Student Loan Repayment Options
When it comes to student loan repayment, there are several options available, each with its own set of features and requirements. The right plan for you will depend on factors such as your income, family size, loan type, and long-term financial goals. Let's dive into the most common student loan repayment plans:
Standard Repayment Plan
The Standard Repayment Plan is the default option for most federal student loan borrowers. Under this plan, you'll make fixed monthly payments for a 10-year repayment period. The monthly payment is calculated based on the total amount of your loans, the interest rates, and the 10-year repayment timeline. This plan is straightforward and ensures that your loans are paid off within a decade, but it may result in higher monthly payments compared to other options.
Graduated Repayment Plan
The Graduated Repayment Plan is designed to accommodate borrowers who anticipate their income will increase over time. Under this plan, your monthly payments start off lower and gradually increase every two years, with the goal of having your loans paid off within 10 years. This can be a good option for borrowers who expect their earnings to rise in the future, as it allows for more manageable initial payments.
Extended Repayment Plan
The Extended Repayment Plan extends the repayment period to 25 years, which can result in lower monthly payments compared to the Standard Repayment Plan. To be eligible, you must have more than $30,000 in federal student loan debt. This plan can be particularly helpful for borrowers with a large amount of student debt who are seeking more manageable monthly payments, but it's important to note that you'll end up paying more in interest over the life of the loan.
Income-Driven Repayment Plans
Income-driven repayment (IDR) plans are designed to make student loan payments more affordable based on your income and family size. These plans include:
Income-Based Repayment (IBR) Plan
The Income-Based Repayment (IBR) plan caps your monthly payments at 10% or 15% of your discretionary income, depending on when you took out your loans. After 20 or 25 years of qualifying payments, any remaining balance on your federal loans can be forgiven.
Income-Contingent Repayment (ICR) Plan
The Income-Contingent Repayment (ICR) plan calculates your monthly payments as the lesser of 20% of your discretionary income or what you would pay on a fixed 12-year repayment plan, adjusted based on your income. After 25 years of qualifying payments, any remaining balance can be forgiven.
Pay As You Earn (PAYE) Plan
The Pay As You Earn (PAYE) plan caps your monthly payments at 10% of your discretionary income and forgives any remaining balance after 20 years of qualifying payments. To be eligible, you must be a new borrower as of October 1, 2007, and have received a disbursement of a Direct Loan on or after October 1, 2011.
Revised Pay As You Earn (REPAYE) Plan
The Revised Pay As You Earn (REPAYE) plan is similar to the PAYE plan, but it has slightly different eligibility requirements and forgiveness timelines. Under REPAYE, your monthly payments are capped at 10% of your discretionary income, and any remaining balance is forgiven after 20 years (for undergraduate loans) or 25 years (for graduate loans).
Income-driven repayment plans can be particularly beneficial for borrowers with lower incomes or who have experienced financial hardship, as they can significantly reduce your monthly payments. However, it's important to note that these plans may result in you paying more interest over the life of the loan due to the extended repayment period.
Loan Consolidation
Loan consolidation is the process of combining multiple federal student loans into a single new loan with a fixed interest rate. This can simplify your repayment by providing a single monthly payment and potentially lower your interest rate. Consolidation also makes you eligible for certain repayment plans, such as Income-Driven Repayment plans, that may not have been available with your original loans.
Loan Forgiveness Programs
In addition to the various repayment plans, there are also several loan forgiveness programs that can help borrowers eliminate their student debt. These include:
Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) Program
The Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) program forgives the remaining balance on your Direct Loans after you have made 120 qualifying monthly payments while working full-time for a qualifying public service employer, such as a government agency or a non-profit organization.
Teacher Loan Forgiveness Program
The Teacher Loan Forgiveness Program offers up to $17,500 in federal student loan forgiveness for eligible full-time teachers who work for five consecutive years in a low-income school or educational service agency.
Military and Veteran Loan Forgiveness
Active-duty military members and veterans may be eligible for various loan forgiveness programs, such as the Army and Navy Student Loan Repayment Programs, which can help pay off a portion of their student debt.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Repayment Plan
When selecting a student loan repayment plan, there are several factors to consider to ensure you choose the best option for your individual circumstances:
Income and Family Size
Your current income and family size are crucial factors in determining the most appropriate repayment plan. Income-driven plans, such as IBR, PAYE, and REPAYE, are designed to make your monthly payments more manageable based on your discretionary income and household size.
Loan Type and Balance
The type and total balance of your student loans can also influence your repayment plan options. For example, the Extended Repayment Plan is only available for borrowers with more than $30,000 in federal student loan debt.
Long-Term Financial Goals
Consider your long-term financial goals and priorities when selecting a repayment plan. If you're aiming to pay off your loans as quickly as possible, the Standard Repayment Plan or a Graduated Repayment Plan may be the best fit. However, if your goal is to minimize your monthly payments, an income-driven plan or the Extended Repayment Plan may be more suitable.
Eligibility for Loan Forgiveness
If you're eligible for a loan forgiveness program, such as PSLF or the Teacher Loan Forgiveness Program, it's essential to choose a repayment plan that aligns with the program's requirements. Income-driven plans are often the best choice for borrowers seeking loan forgiveness.
Navigating the Application and Recertification Process
Applying for and maintaining enrollment in a student loan repayment plan can involve several steps and ongoing requirements. Here's a general overview of the process:
Applying for a Repayment Plan
To apply for a specific repayment plan, you'll need to complete an application form, which is typically available on your loan servicer's website. The application process may require you to provide information about your income, family size, and other financial details.
Recertifying Your Income
For income-driven repayment plans, you'll need to recertify your income and family size annually to ensure your monthly payments remain aligned with your current financial situation. Failing to recertify on time can result in your monthly payments reverting to the Standard Repayment Plan amount.
Documenting Qualifying Payments
If you're pursuing loan forgiveness through a program like PSLF, it's essential to carefully document your qualifying monthly payments and employment history. This includes submitting an Employment Certification Form (ECF) to your loan servicer on a regular basis.
Monitoring Your Repayment Progress
Regularly reviewing your student loan statements and repayment progress is crucial to ensure that your payments are being properly applied and that you're on track to achieve your repayment or forgiveness goals.
Case Studies and Examples
To better illustrate how student loan repayment plans can be applied in real-world scenarios, let's explore a few case studies:
Case Study 1: The Recent Graduate
Sarah, a recent college graduate, has $35,000 in federal student loans with an average interest rate of 5%. Her starting salary is $45,000 per year. Given her financial situation, the best repayment plan for Sarah would be the Revised Pay As You Earn (REPAYE) plan. Under REPAYE, her monthly payments would be capped at 10% of her discretionary income, which is approximately $250 per month. After 20 years of qualifying payments, any remaining balance on her loans would be forgiven.
Case Study 2: The Public Servant
John, a social worker, has $65,000 in federal student loans with an average interest rate of 6%. He works for a non-profit organization and is interested in pursuing the Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) program. The best repayment plan for John would be the Income-Based Repayment (IBR) plan, as it aligns with the PSLF program's requirements. Under IBR, John's monthly payments would be capped at 10% of his discretionary income, which is approximately $350 per month. After 10 years of qualifying payments while working in public service, any remaining balance on his loans would be forgiven through the PSLF program.
Case Study 3: The Veteran
Jessica, a U.S. Army veteran, has $25,000 in federal student loans with an average interest rate of 4.5%. As a veteran, she is eligible for the Army Student Loan Repayment Program, which can help pay off a portion of her student debt. Additionally, Jessica may consider the Income-Contingent Repayment (ICR) plan, which would cap her monthly payments at 20% of her discretionary income, which is approximately $200 per month. After 25 years of qualifying payments, any remaining balance on her loans would be forgiven.
Tips for Successful Student Loan Repayment
To help you navigate the student loan repayment process and achieve your financial goals, here are some valuable tips:
Stay Informed and Proactive
Regularly review your student loan statements, understand your repayment options, and stay up-to-date on any changes or updates to the various repayment plans and forgiveness programs. Being proactive and informed can help you make the best decisions for your financial situation.
Communicate with Your Loan Servicer
Maintain open communication with your loan servicer, as they can provide valuable guidance and support throughout the repayment process. If you're experiencing financial hardship or need to adjust your repayment plan, don't hesitate to reach out to your servicer.
Explore Refinancing Opportunities
If you have private student loans or a high-interest federal loan, consider refinancing to potentially lower your interest rate and monthly payments. However, be mindful that refinancing federal loans may make you ineligible for certain repayment plans and forgiveness programs.
Prioritize Paying Extra When Possible
If your financial situation allows, consider making additional payments towards your student loans, even if it's a small amount. This can help you pay off your loans faster and reduce the overall interest you'll pay over the life of the loan.
Seek Professional Guidance
If you're unsure about the best repayment strategy for your specific situation, consider consulting with a financial advisor or a student loan expert who can provide personalized guidance and help you navigate the complexities of student loan repayment.
Conclusion
Navigating the world of student loan repayment can be overwhelming, but with the right information and a strategic approach, you can successfully manage your debt and achieve your financial goals. By understanding the various repayment plans, eligibility requirements, and forgiveness programs, you can make informed decisions that align with your unique circumstances. Remember to stay proactive, communicate with your loan servicer, and seek professional guidance when needed. With the right plan in place, you can take control of your student loans and move forward with confidence.
KEYWORDS: student loan repayment plans, income-driven repayment, loan forgiveness, loan consolidation, student debt management
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0































































